Credssp Encryption Oracle Remediation
- Jan 28, 2019 1 The client has the CredSSP update installed, and Encryption Oracle Remediation is set to Mitigated. This client will not RDP to a server that does not have the CredSSP update installed. 2 The server has the CredSSP update installed, and Encryption Oracle Remediation is set to Force updated clients. The server will block any RDP connection from clients that do not have the CredSSP update.
- Nov 03, 2018 Method 1: Solving CredSSP Encryption Oracle Remediation Problem using Registry Editor Open Registry Editor First, you need to open Registry Editor in your Windows 10 PC or Laptop. Expand HKEYLOCALMACHINE. This will open Registry Editor in a new window. Navigate to System Registry.
I am unable to see the option 'ENCRYPTION ORACLE REMEDIATION' in the group policy. My Remote computer is Windows 8.1 Pro & client PC is Windows 8.1 Thank you in advance. Whitney - Thursday, June 28, 2018 1:02:37 AM; Hi, I am unable to see the option 'ENCRYPTION ORACLE REMEDIATION' in the group policy.
“Patch Lady” Susan Bradley has some on AskWoody about Microsoft, “CredSSP updates for CVE-2018-0886.” She mentions that you can prepare for the updates by setting group policy before they are installed. However, I found that the group policy settings is not available on a domain controller if the update is not installed.Update May 10, 2018 Please see updates at the end of the post before applying any group policy!The problem is that you need the new admx (policy) and adml (resource) files that are delivered with the patch. For group policy wonks, this is no doubt old hat, but for the rest of us:1. Find a machine with the latest security update installed. If you’re like me, you’re deferring updates, so this may take some hunting.
This issue affects all versions of Windows; check for a list of KB numbers by Windows version. I finally found the update applied to a Windows 7 virtual machine that I allow to update automatically.2. Copy these two files from that machine to a temporary location:C:WindowsPolicyDefinitionsCredSsp.admx (dated 2/9/2018)C:WindowsPolicyDefinitionsen-USCredSsp.adml (dated 2/10/2018; adjust language folder to your local language)3.
On a domain controller, in Windows Explorer, navigate toC:WindowsSYSVOLsysvolPoliciesPolicyDefinitionsa. Rename the current CredSsp.admx to CredSsp.admx.old, or move it to another location.b. Copy the CredSsp.admx file from the updated machine to this folder.Note If you try to open the group policy at this point, you’ll get this error:You need the resource file too.4. On a domain controller, in Windows Explorer, navigate toC:WindowsSYSVOLsysvolPoliciesPolicyDefinitionsen-US (or your local language)a. Rename the current CredSsp.adml to CredSsp.adml.old, or move it to another location.b.
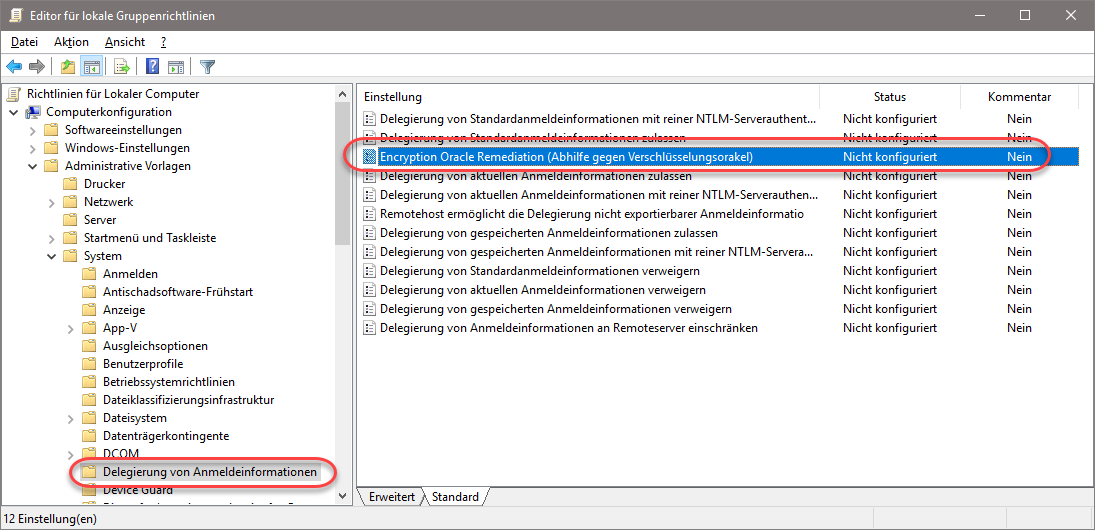
Copy the CredSsp.adml file from the updated machine to this folder.You should now be able to edit the new group policy:Computer Configuration Policies Administrative Templates System Credentials Delegation Encryption Oracle RemediationUpdate March 17, 2018Do not set Encryption Oracle Remediation to Mitigated on unpatched servers or you will lose the ability to RDP from patched clients. See the matrix at the bottom of. As per my post on – these are the steps we’re employing to deploy this to our clients:1. Install patch on all servers and clients2. Configure GPO for servers with:Computer Configuration - Administrative Templates - System - Credentials Delegation - Encryption Oracle Remediation and (initially) set to Mitigated (1)3. Configure GPO for clients with:Computer Configuration - Administrative Templates - System - Credentials Delegation - Encryption Oracle Remediation and (initially) set to Vulnerable (2)4.
Test RDP functionality – should be OK5. For clients that rely on RDP – check WSUS to confirm that all clients have the relevant patch – refer for the KB numbers. Then warn staff of pending security improvement.6. Prepare for manual update/installation of patch for unpatched clients that may surface in next step.7. Change client GPO setting from Vulnerable (2) to Mitigated (1)8. Handle collateral damage J9. Change server and client GPO settings from Mitigated (1) to Force updated clients (0).
Don, Mark, confirming that we apply the two policies on a role basis – so it’s less to do with the OS and more to do with the role of the device, as determined by the OU the device is located in. This has allowed us to enforce the updated CredSSP on our servers, whilst relaxing the enforcement on our client computers so we can still connect to clients’ servers that are yet to be patched.It’s a pity that Microsoft didn’t consider the two different roles in defining the policy, that way we could get away with a single GPO object applied at the domain level.
I had a handful of Windows 10 systems (mostly home users) that dropped the 1803 build last night that have had trouble connecting to our RDSS on Windows 2008 R2 as of this morning. The server was last patched in early April. For some reason it did not get the relevant updates/patches that it should have starting with the March updates. I ended up installing KB4088878 manually which is now allowing the Windows 10 clients with the 1803 build to successfully connect. What I don’t understand is why the registry entry(HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesSystemCredSSPParameters) is missing on the Windows Server 2008 R2 server. Sandeep’s post initially included a link to a blog post, which asks you to download a.zip file from Google Drive, which then opens a.reg file, which will set AllowEncryptionOracle = 2 (Vulnerable). The article says that this “This works 100%.”If you don’t see the red flags, here they are:1.
Don’t trust articles that don’t explain why they ask you to do something.2. Don’t download files from unknown/untrusted sites.3. Don’t open zip files from unknown/untrusted sources. (I scanned it first at.)4. Don’t apply.reg files if you don’t know what they do.In this case, the file is not a virus, but its entire intent is to override the new CredSSP security mitigation and make sure that your systems remain vulnerable forever. All without any explanation, just claiming that this solution solves the issue “in a single click.”My advice: do NOT set your systems to Vulnerable unless you need that as temporary workaround. Much better is to patch both servers and clients, then remove the group policy or manual registry entries entirely so that the vulnerability is Mitigated.
Gerry, the reg key and/or group policy can be used to override the default behavior. As of May 2018, the default is Mitigated, so If you have patched the server and clients, you should not need or see any reg keys.In fact, I have now Undefined and then deleted the group policy that I set up when I wrote this article in March. It’s no longer needed.

Credssp Encryption Oracle Remediation Server 2012
(I Undefined it first and let it update. That removed the reg key.
Then after the reg key was removed on all machines, I deleted the group policy.).
Remote Desktop connectionAn authentication error has occurred.The function is not supported.Remote Computer: hostnameThis could be due to CredSSP encryption oracle remediation.This error is caused by the fact that on Windows Server or desktop Windows versions, to which you are trying to connect using RDP, since March 2018 there were no security updates installed. In March 2018, Microsoft released an updates that blocks remote code execution using a vulnerability in the CredSSP protocol (bulletin CVE-2018-0886). After successfully connecting to a remote RDP server (computer), you need to install the missing security updates on it through the Windows Update (verify that the service is enabled) or manually. Below are direct links to updates for Windows Server, which must be installed:. Windows Server 2012 R2 / Windows 8 –. Windows Server 2008 R2 / Windows 7-.
Windows Server 2016 / Windows 10 1607 –After installing the updates and rebooting the server, don’t forget to disable the policy on the clients (either switch it to the Force Updated Clients), or return the value of the AllowEncryptionOracle registry parameter to 0. In this case, your computer will not be at risk of connecting to unprotected hosts with CredSSP and exploitation of the vulnerability.REG ADD HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesSystemCredSSPParameters /v AllowEncryptionOracle /t REGDWORD /d 0. RADJ,Sorry I’ve just seen your replyQ: Have you disabled NLA on the server side? A: YesQ: Do you use Windows Server 2003 / Win XP or something similar as an RDP server? A: NoQ: What is the Windows version on the client?
A: Windows 7Q: Did you enable the policy Oracle Remediation Encryption = Vulnerable on the client computer? A: NoAs the server can’t be updated, it doesn’t has that group policy to configureSo the quick fix was to deselect that box.In this other site I saw a regedit solution:Reply. Most likely the AllowEncryptionOracle = 2 registry parameter on computers with Windows XP will not work. Most likely, to connect to RDS from clients on XP, you need to switch the Encryption Oracle Remediation policy to the Mitigated/ Vulnerable level on terminal servers. However, the RDS server will be vulnerable to the exploitation of the CredSSP vulnerability (CVE-2018-0886). You will also have to disable the Network Level Authentication on RDS server (however, there is also a workaround for enabling NLA in Windows XP SP3). Those, it should be used only as a temporary solution, until you update the OS on clients to Windows 10 / 8.1 / 7.